Data Analysis
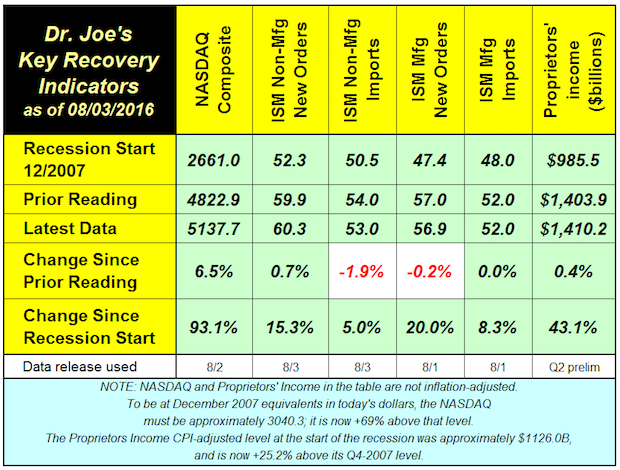
Recovery Indicators: 3 Up, 2 Down, 1 Unchanged
Published: August 4, 2016
The NASDAQ had a good month, rebounding by 6.5% last month. Compared to last year at this time, the NASDAQ is up +0.6%, which is a negative return compared to inflation (less inflation it is -0.5% because the CPI is +1.1%). Full Analysis
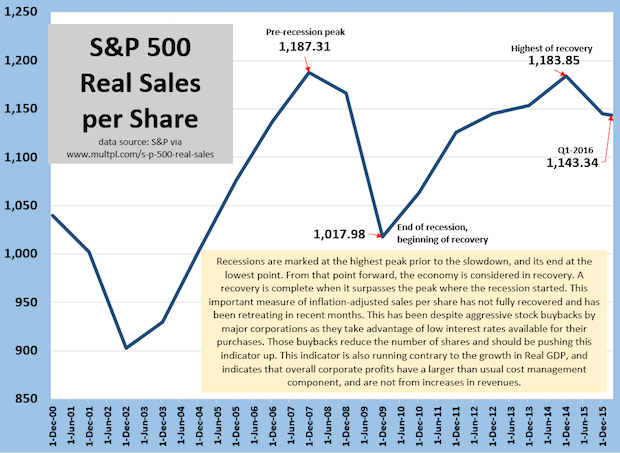
S&P 500 Real Sales per Share Reflects Struggling Economy
Published: July 28, 2016
A way of judging the health of the economy is to calculate the inflation-adjusted sales of all of the companies in the S&P 500 and divide it by the total number of public shares. This index should have a natural upward bias. S&P 500 companies are very large, and acquire or merge with other companies, many of which are outside of the 500 companies. Buybacks of stock, which has been a trend of note these last five or so years, reduce the number of shares, or slow the growth in shares, reduce the denominator, again, giving it an upward bias. Instead, this measure has suffered. It peaked in 2007, and has yet to surpass that level. This means that corporate profits, which have generally been good (though slowing lately) have been managed by refinancing of debt to lower interest rates and reductions in costs and expenses. Those better profits are not the result of increased revenues. Slow, sluggish economic growth is reflected in these figures, and is a reminder that one should not look only to GDP as an indicator of the true health of the private sector. Full Analysis
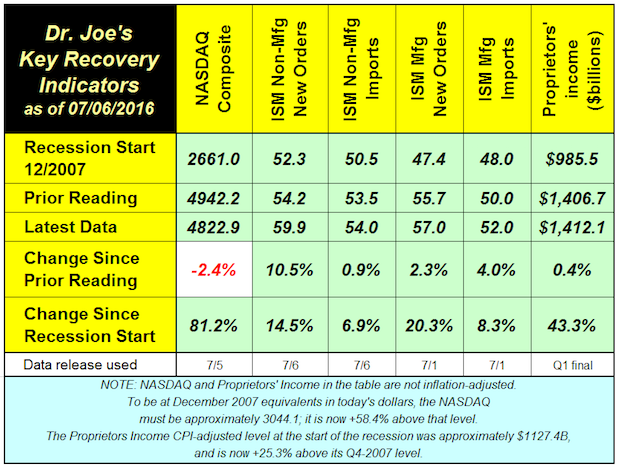
Recovery Indicators Better than Recent Economic News
Published: July 7, 2016
The recovery indicators showed better economic activity in June. This ended the second quarter in a manner that seemed contrary to many recent economic data. Full Analysis
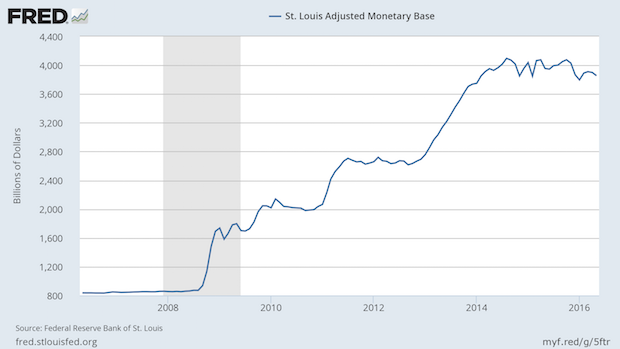
Are We Headed to QE4?
Published: July 7, 2016
This chart shows the Fed's balance sheet in the format known as the St. Louis Adjusted Monetary Base. Prior to the doubling of that balance sheet, it was growing at the annual rate of 6%, which was basically comprised of the long term rates of 1% for population growth, 2% for inflation, and 3% for economic growth. Full Analysis
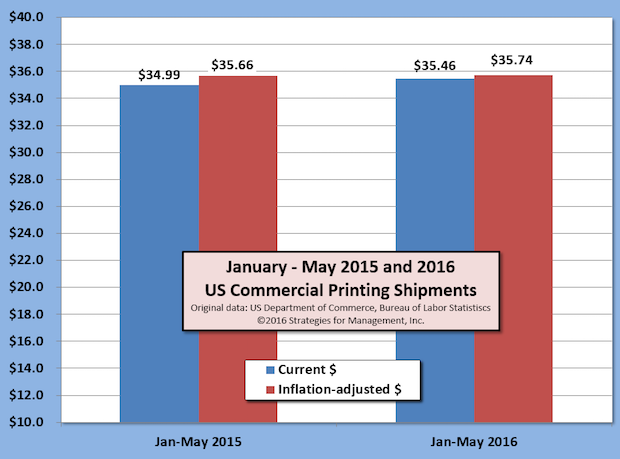
May Printing Shipments Up +1.2% Versus 2015; Trend is Flattening
Published: July 6, 2016
US commercial printing shipments for May16 were $7.37 billion, the highest level in current dollars for the month since 2013. For the first five months of 2016, shipments are up approximately +$476 million in current dollars (+1.4%) and up +$79 billion after inflation (+0.2%) Full Analysis
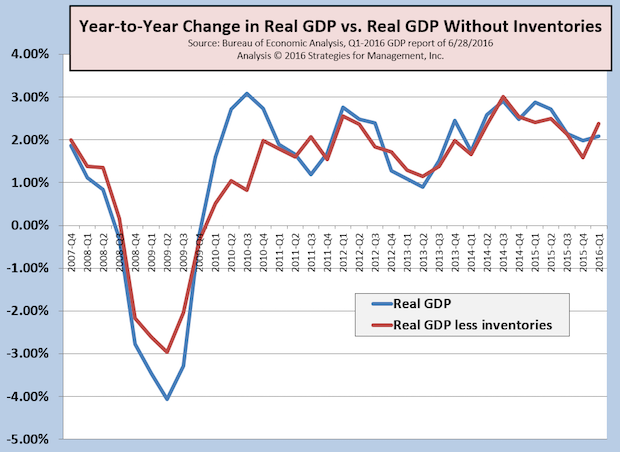
US Q1-2016 GDP Revised to +1.1%
Published: June 30, 2016
US real GDP for Q1-2016 had its third and final revision in this reporting cycle, and was +1.1% on an annualized basis compared to Q4-2015. Q1 had been reported as +0.5% in its advance report, +0.8% in the preliminary report, and now as +1.1%. Real GDP remains very low compared to the post-WW2 +3.3% rate. Full Analysis
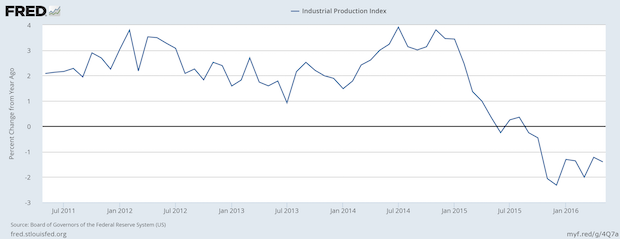
Industrial Production Continues its Negative Turn
Published: June 23, 2016
The Fed’s own data probably caused them to have a more dour outlook about the economy. The chart shows that US industrial production started slowing at the end of 2014 and has been in outright contraction since Fall 2015. Full Analysis
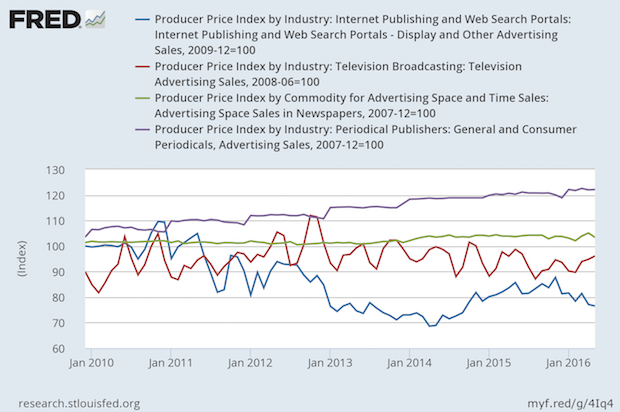
Prices for Advertising Rise for Magazines, Stable for TV and Newspapers, Down for Digital
Published: June 16, 2016
The chart shows that magazine advertising has gone up by more than 20% since 2010, but it's hard to know how much might have been bundled in those prices. Pricing reports sent to the Bureau of Labor Statistics are supposed to be in constant units, but it's hard to determine those in service environments, and it's hard to quantify a wink or a nod in an advertising agreement. Full Analysis
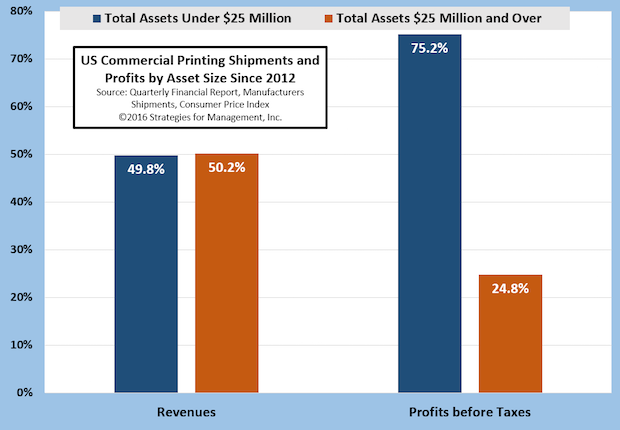
Smaller Printers Are Giants in Profits
Published: June 9, 2016
The changes in the media markets led to the declines in magazines, catalogs, newspaper inserts, and many of the products produced by large printing organizations. For years, these companies were giants in the industry, but recently this sector has been restructuring through consolidations. Writedowns in goodwill and for closed plants have cut the profits of these organizations. Full Analysis
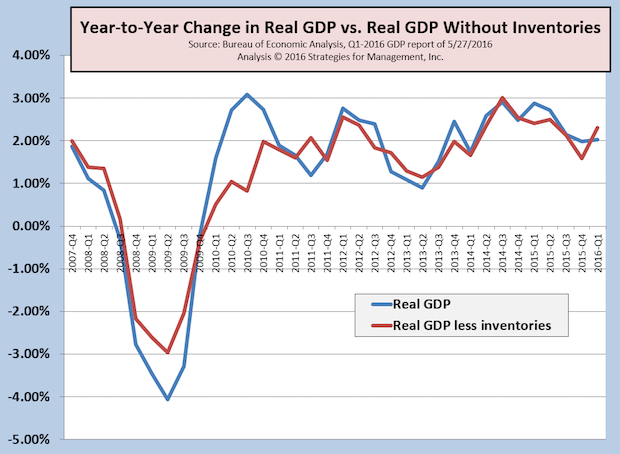
Q1-2016 Real GDP Revised Up to +0.8%; Economy Already Recovering from Mini-Recession
Published: June 2, 2016
The first estimate of Q1-2016 GDP was +0.5%, and that was revised up slightly to +0.8%. The concerns about recession are being reduced lately with some better economic news that show the economy on its sluggish pattern of sub-par growth in the +2% range, well below the post-WW2 average of +3.3%. As noted many times, there are numerous economic indicators that have yet to reach their pre-recession levels. Since this pattern has been so long in duration, even non-money denominated statistics, such as employment, have to be adjusted by population growth to discern true underlying levels. The chart shows Real GDP on a more conservative year-to-year basis as reported and with the volatile effects of inventory changes removed. The economy still seems to be digesting some long-term inventory rebalancing, some of which is related to global currency and other economic issues. The slowdown of the first quarter still seems to be limited to the first six weeks of the year. At the time of this writing, the Atlanta Fed's GDPNow estimate of Q2-2016 is at +2.5%. While that is a disappointing level, it is consistent within the lackluster level of economic growth that has come to be known these past years as “new normal.” Since 2011, real GDP has averaged only 2%. The difference in the average may not seem a lot, but a 2% annual growth rate will result in an economy doubling in size in 39 years; at 3.3%, it doubles almost 16 years sooner.
Full Analysis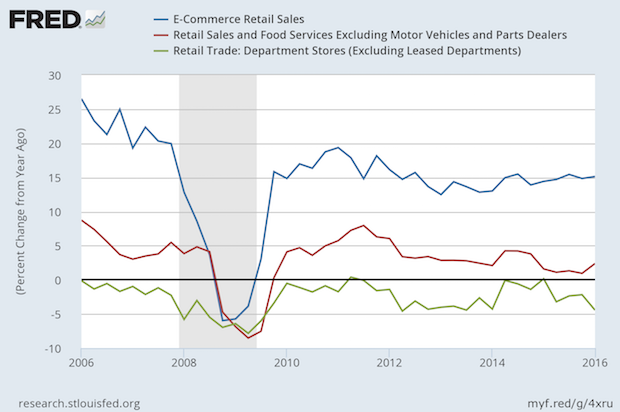
Retail Sales Growth Rates Reflect Changes in Competition and Consumer Preferences
Published: May 26, 2016
Department stores are still having problems. Their year/year growth rate has been negative for more than a decade. E-commerce sales are maintaining a 15% growth rate. At that rate, they double every five years. The last peak in growth for retail sales excluding motor vehicles was in late 2011, and that rate, unadjusted for inflation, has slowed to the 2% range. Retail sales are a function of household income, and their costs, and they remain sluggish as median household income has still not reached the level it was at the beginning of the recession. In the meantime, shopping malls, the department stores that anchor them, and mall owners are having problems. A Weekly Standard article about Amazon has some insights into it. The downslide of brick and mortar retail stores and malls can create collection problems for printers who sell to them, but there are changes underway that might hold some opportunities for those printers who seek them. Developers are using mall complexes for new buildings that include office space and even hospitals and hockey rinks. There are also new efforts to treat the shopping experience not just as a matter of location, but holistically to include all digital touchpoints inside and outside the mall. How will much of this be communicated? It will often require signage, working closely with store owners and local mall management. Those printers, attuned to the nature of communications logistics and data management, can find opportunities there.
Full Analysis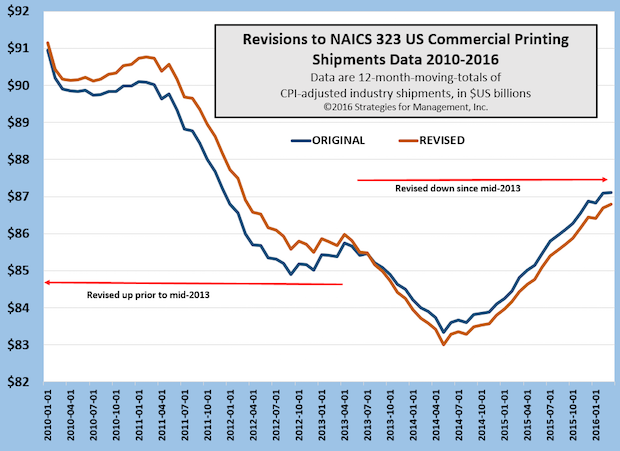
Printing Industry Shipments Revised from 2007 to 2016, with Minor Changes Since 2009
Published: May 19, 2016
The years 2008 through 2013 had slight revisions higher; the end of 2013 to present had slight revisions lower. The Commerce Department's revisions to all manufacturing data are leading up to a multi-year revision of GDP data at the end of July. Full Analysis
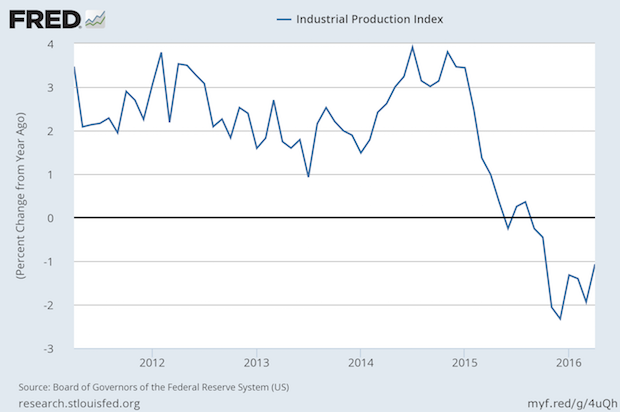
Manufacturing Still in Contraction
Published: May 19, 2016
The latest Federal Reserve industrial production index showed a slowdown since late 2014 and an outright contraction since mid-2015 is still in process. The business press focused on the comparison to the prior month, which looked like an improvement. The chart, however, compares to the prior year. Recent consumer retail data have been more optimistic, and the premise that we had a “micro-recession” at the beginning of the first quarter seems to be justified. There is growing pressure to weaken the US dollar to make manufacturing exports less expensive to international customers. The Atlanta Fed's GDPNow estimate for Q2 GDP is now +2.5%. At that rate, it would be a rebound from Q1's +0.5%. Full Analysis
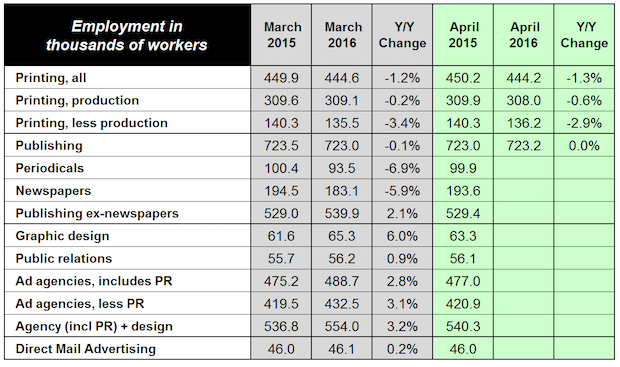
Graphic Design Employment Up +6%, Agencies up +2.8%
Published: May 12, 2016
Content creation is in a strong uptrend based on the latest employment data. Graphic design employment is up +6%, and has taken over from public relations employment as the surging area of hiring. Full Analysis
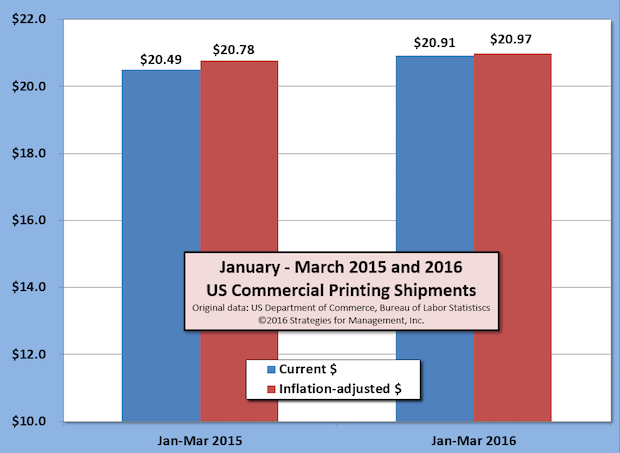
19 Consecutive Months of Improved US Commercial Printing Shipments
Published: May 5, 2016
US commercial printing shipments have increased compared to the prior year for 19 consecutive months. March 2016 shipments were up +$85 million (+1.1%) in current dollars compared to 2015, and +$22 million (+0.3%) after adjusting for inflation. February 2016 shipments were revised up by $2 million. Full Analysis
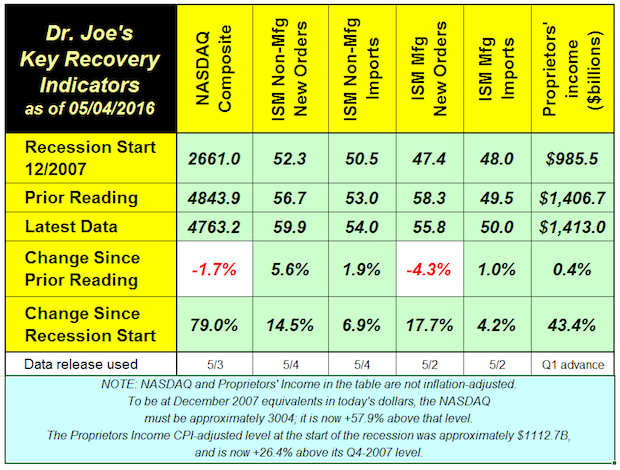
Recovery Indicators Better than the Recent General Economic News
Published: May 5, 2016
The recovery indicators are more positive than the general economic news. One of our indicators, the NASDAQ, is down -1.7% since last month. It's been on a rocky road for the last three quarters. Its recent peak was 5218.86 in July, and it has not gotten really close since. Stock market concerns have focused on a decline in the rate of corporate profits, and Apple's recent financial report did not really help matters. There was a bullish rise in non-manufacturing orders. Manufacturing new orders index might look like a decline, but it is still indicate moderate growth. Proprietors income, a measure of the health of small business, was up only slightly. Other reports of small business health have not been good, especially the recent NFIB Small Business report. This month's recovery indicators don't indicate recession, a word that is bandied about with greater frequency lately, but support the continuing unsatisfying levels of slow but positive growth. Full Analysis
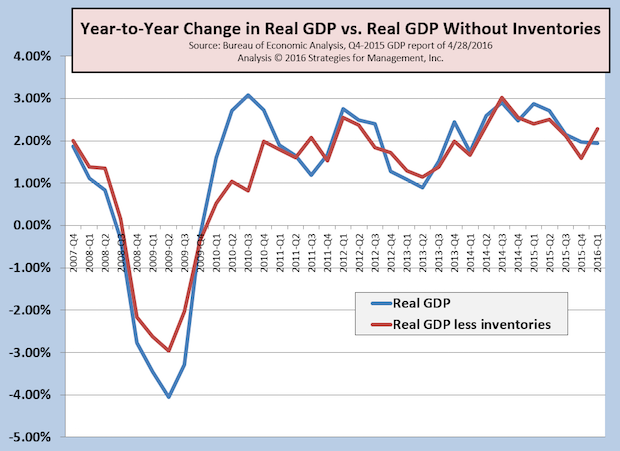
Q1-2016 GDP +0.5%; Inventory Correction Finally Arrives
Published: April 29, 2016
US real GDP for Q1-2016 was reported at annual growth of only +0.5% compared to Q4-2015. On a year-to-year basis, the growth rate was +1.95%. The inventory adjustment that the economy has needed finally came, with the lowest net inventories in two years. Real GDP growth less inventories was +2.3% on a year-to-year basis. Full Analysis
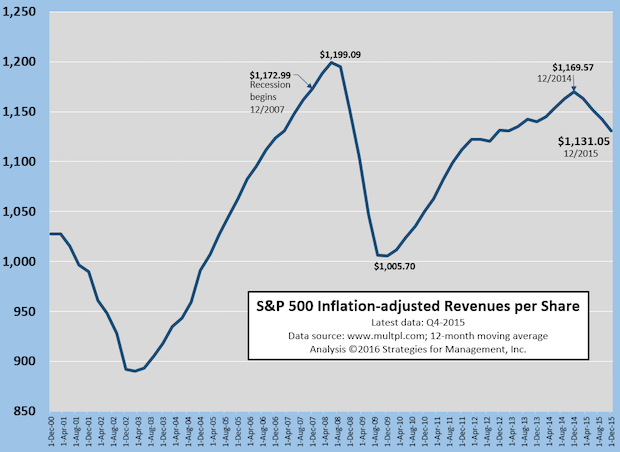
S&P 500 Revenue Per Share Still Lags Economy
Published: April 28, 2016
Everyone knows that the stock market is up from its lows at the bottom of the recession,but one obscure but key measure underscores how sluggish the economy has been. The S&P 500 should have a bias of steadily increasing revenues. It has most of the best companies in the world, with international presence in the globe's growing markets and a foundation in the established ones. It is rare for companies to be dismissed from the S&P 500, but companies are added all the time. When S&P companies merge, they create a new entity of combined revenues, and another company is added with new revenues to add to the index. The other upward bias should be the high level of stock buybacks buy these large companies, as they borrow money at low interest rates and create “shareholder value” by reducing the number of shares and increasing the value of each share of stock. We've called this cowardly, as it increases earnings per share (EPS) without needing to increase total profits. So this revenue per share should be steadily increasing with a growing economy in a recovery that started in mid-2009. It seems that companies have done a much better job of financial engineering than they have in creating revenues. Full Analysis
NFIB Small Business Index: A New Recession for Main Street?
Published: April 21, 2016
Economic data have been conflicting of late, but there is one consensus in the data that is clear: the small business economy did not recover from recession, and looks like it’s back in recession territory. There are many indicators we use for small business but one that is watched often is that of the NFIB. It is published monthly and has a long history. US government data focuses attention on the largest businesses because they represent big chunks of the economy and report some kind of data, especially payroll data, with great frequency. Think of it as counting whales rather than minnows. Their recent analysis said “The small business sector... is underperforming, doing little more than operating in maintenance mode. Slow economic growth is now just a result of population growth, more haircuts, retail customers, health care patients, etc. But there is no exuberance, no optimism and not much hope, the numbers make it clear.” Economies stuck in +2% growth mode tend to do that. Full Analysis
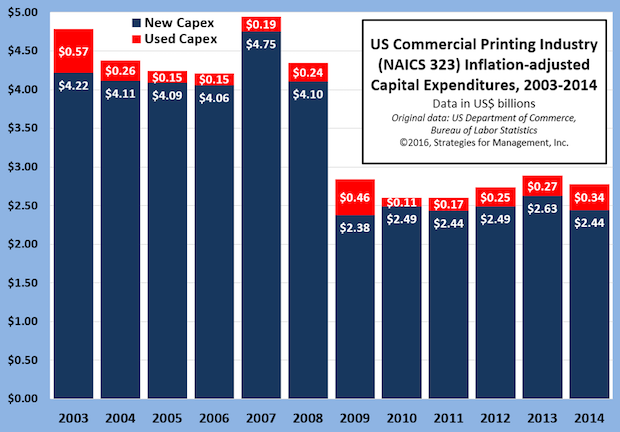
2014 US Commercial Printing Capital Expenditures: New Purchases Down, Used Purchases Up
Published: April 19, 2016
The US Department of Commerce recently released its Annual Survey of Manufactures Capital Expenditures report, issuing data for 2014. Full Analysis
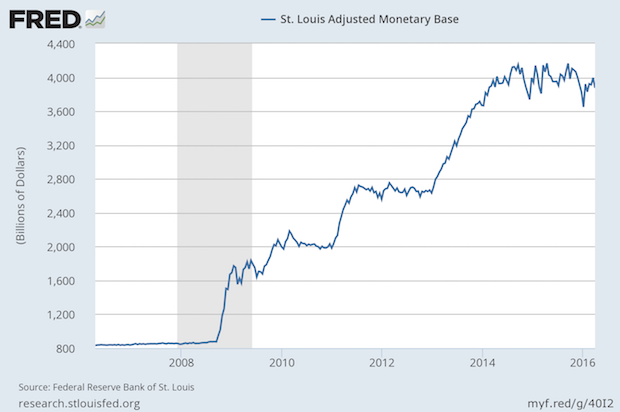
The Fed Never Really Stopped QE3
Published: April 14, 2016
This week’s chart shows the aggressive actions of the Federal Reserve after the housing bubble. For decades, the Fed’s balance sheet increased by about 6% per year, averaging about half inflation and half economic growth. The rocket-like rise when the bubble burst is clear, and then the three steps up of each of the quantitative easings are plainly seen. The Fed has wanted to raise rates for some time, but they have also wanted to stop the buying of government instruments that characterized the QE programs. They create shortages of publicly traded bonds which increases their prices, which makes the effective interest rates low. Rather than ending their purchases, the Fed has been replacing matured obligations. In effect, this keeps QE3 going. Can the Fed ever end it? They may hold on and hope that over time that economic growth and inflation catches up to them in time, but that can take forever, or perhaps longer. It will be difficult for the Fed to end its policy without robust economic growth that will give them the flexibility and opportunities to unwind their holdings. Should a recession begin, or a new financial crisis emerge (even an internationally) the Fed might need to create an additional QE effort. Full Analysis
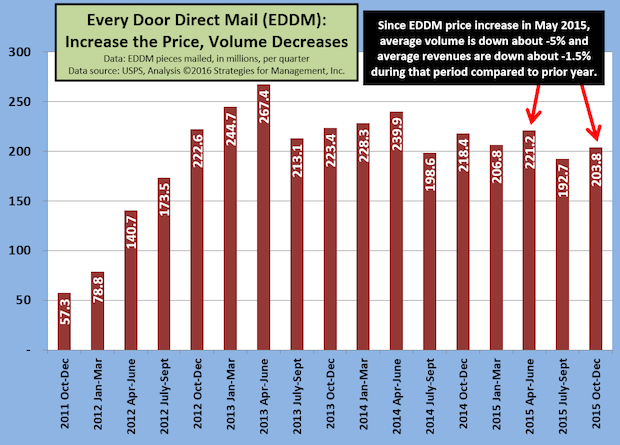
Can USPS Price Increase Rollback Get EDDM Moving Again?
Published: April 7, 2016
The USPS is always in the news, and last month's Annual Compliance Determination report was not particularly positive. “The majority of products failed to meet service performance targets for FY 2015” read the Postal Regulatory Commission press release. The PRC directed “the Postal Service to improve service performance and provide a comprehensive plan within 90 days.” Full Analysis
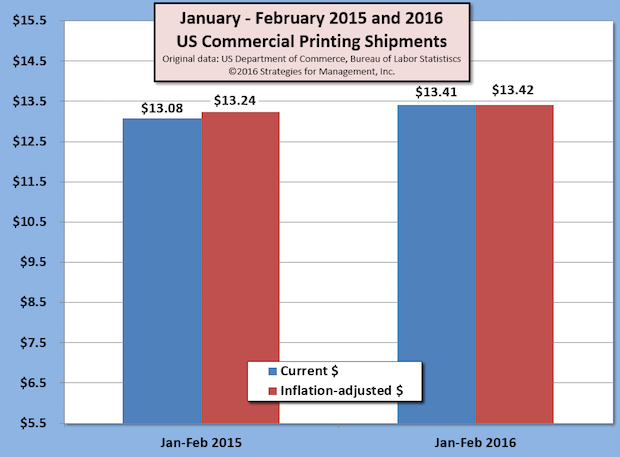
Twenty-one Months of Consecutive Increases for US Commercial Printing Shipments
Published: April 6, 2016
The US Department of Commerce issued its latest report of US commercial printing shipments (NAICS 323) and the data show 21 consecutive months of positive comparisons to the prior year current dollar shipments. The trend started with June 2014, and has been an average increase of +3.3%, +$225 million per month, for that period. Full Analysis
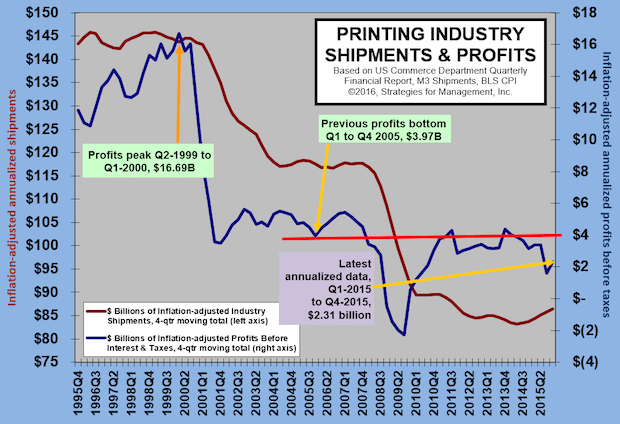
Printing Profits Rebound (A Little)
Published: March 31, 2016
Profits bounced back from a terrible third quarter which had an industry-aggregate loss of -2.57% as a percentage of revenues, and went back up to a more reasonable 4.38%. The difference was the massive writedowns of the third quarter which resulted in a -10.97% loss in printing companies with more than $25 million in assets. Full Analysis
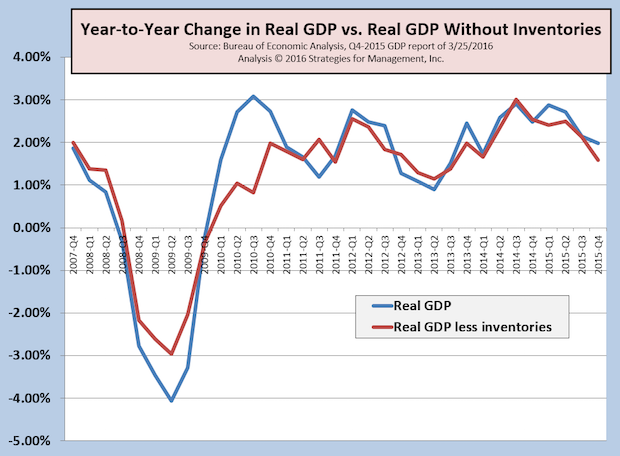
Third Look at 4Q-2015 GDP Revised Up, Atlanta Fed Q1-2016 GDP Estimate Plummets
Published: March 30, 2016
In a clear case of dealing with a two-handed economist when asked about economic conditions, the Bureau of Economic Analysis increased their estimate of fourth quarter GDP to +1.4%. The initial report was +0.7%, and then it was revised to +1.0%, and now it is +1.4%. They were off only by $100 billion from the first report, greater than the size of the printing industry, just to add some perspective about how big the US economy is. Full Analysis
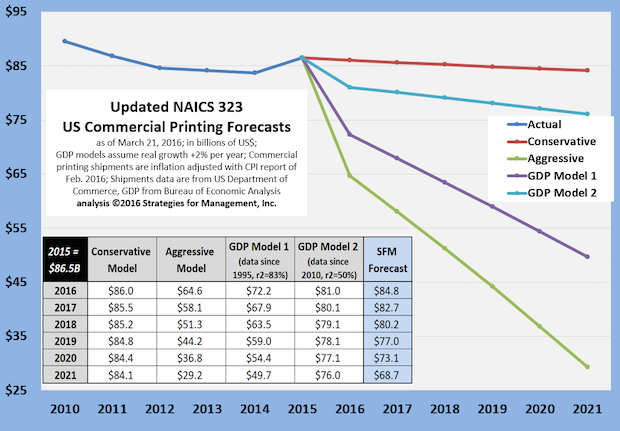
Updated Commercial Printing Forecasts to 2021
Published: March 24, 2016
Now that 2015 data are complete, we have run the forecasting models again and present them in this chart. Full Analysis
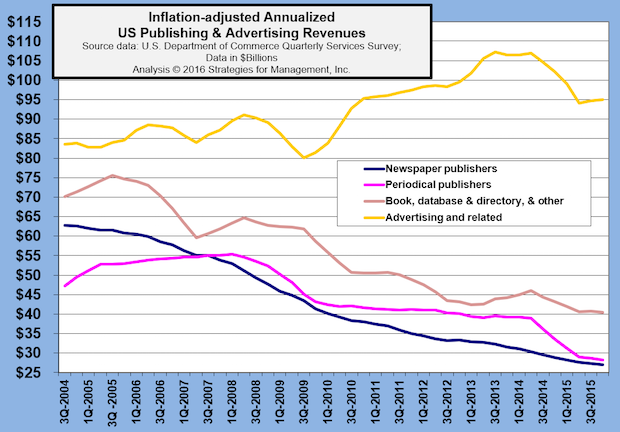
Advertising Agency Revenues Have Major Revision Down for 2013 & 2014, but Remain in Long-term Uptrend
Published: March 17, 2016
The US Department of Commerce released its latest Quarterly Service Survey last week, and it reduced shipments for the third quarter of 2013 by -$4 billion (whoops – a -15% statistical error). Full Analysis
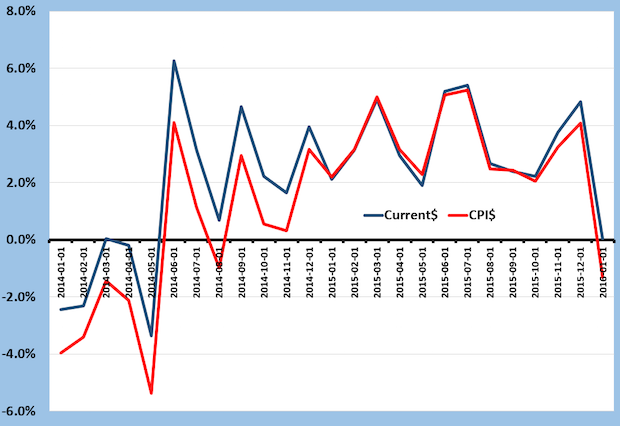
Is the Positive Run for Commercial Printing Coming to a Close?
Published: March 10, 2016
The latest printing shipments were discussed in the “Mondays with Dr. Joe” of March 7. The chart offers more details. Revenues turned around on a current dollar basis with June 2014 shipments (blue line) and the positive comparisons to the prior year kept going until the most recent report, January 2016. In current dollars, January’s shipments were barely above those of 2015, keeping the positive comparison streak intact. Full Analysis
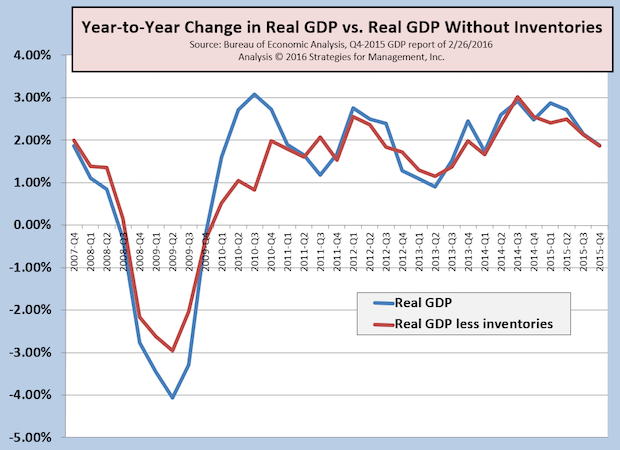
4Q-2015 GDP Revised Up from +0.7% to +1.0%, But Not as Good as It Seems
Published: March 1, 2016
The second estimate of fourth quarter GDP was revised up from +0.7% to +1.0%, mainly from an increase in net inventories. This factor in the GDP calculation is volatile, so we track GDP with and without it to get a perspective of the underlying GDP rate from a long term perspective in a year-to-year comparison. Full Analysis
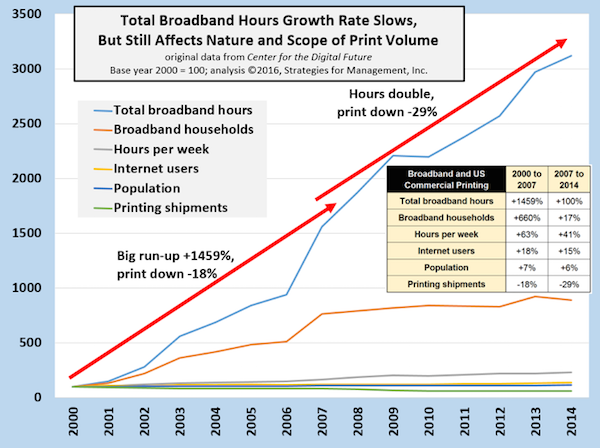
Broadband Hours and US Commercial Printing
Published: February 26, 2016
In 2014, US per capita hours using broadband is just over 900 per year (2.5 per day), and that's the entire population. The number of total hours has doubled since 2007. The population has grown in that period, but the average number of hours online per week has gone from 15.3 to 21.5 in 2014, and households with broadband connections grew from 76% to 89%. The cumulative effect has had most of its effect on mainstream commercial printing, especially information materials used for promotion and product support and advertising-funded products like magazines and catalogs. Printing's use is becoming more tactical, focused on specialty uses of printed images with higher expectations for impact, especially in concert with other media. Full Analysis
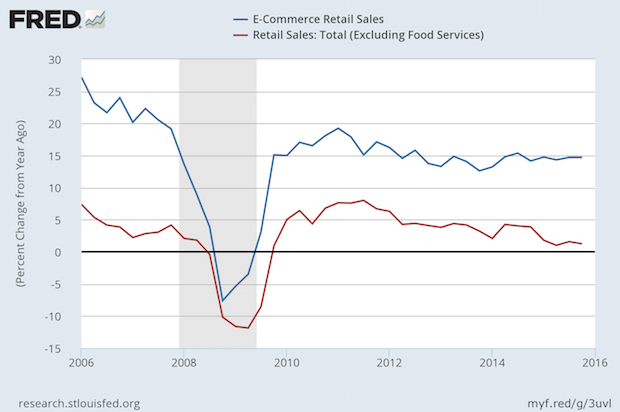
E-Commerce Retail Sales Still Growing at Nearly 15% Per Year
Published: February 18, 2016
E-commerce sales of all types, including industrial products, is still growing at a rate just under 15% per year. Full Analysis
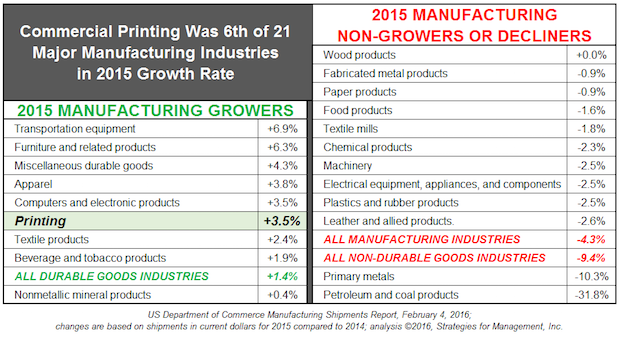
Printing Was 1 of 8 Major Manufacturing Industries with Positive Growth in 2015
Published: February 11, 2016
Part of print's good 2015 was how well it did compared to other industries. Of 21 major manufacturing industries, nine had positive years in current dollars, with commercial printing as sixth highest. Precipitous decreases in commodities prices caused manufacturing in metals and energy to have such a bad year that the entire manufacturing sector declined -4.3%. For the year, current dollar GDP growth was +2.9%. For the first time in twenty years, commercial printing growth exceeded GDP. Full Analysis
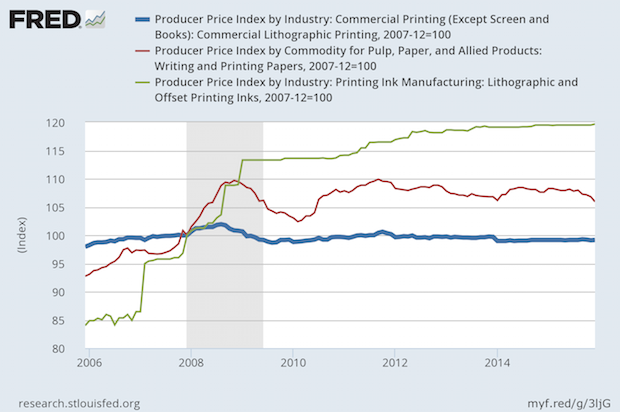
Commercial Printing Prices Less Than December 2007; Paper and Ink Higher
Published: February 4, 2016
Since December 2007, the CPI is up by +12.6%. How have the PPI for commercial printing, ink, and paper changed? Commercial printing prices are lower, -0.8%. This means that a commercial printing business has to increase its productivity and profitability to reward its owners and employees to make up for the loss of purchasing power they have in their paychecks. Full Analysis
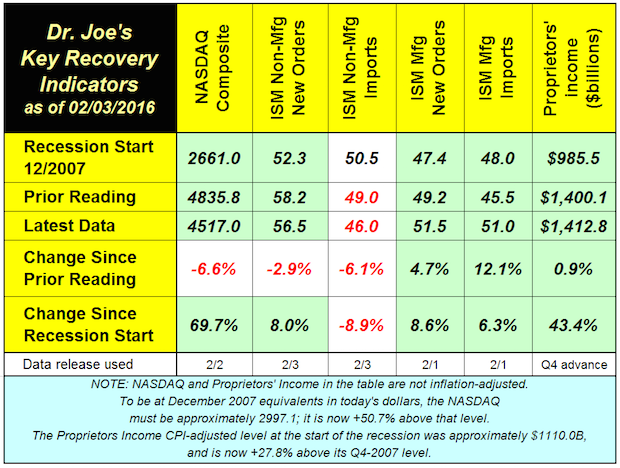
Recovery Indicators Show Economic Slowdown Underway
Published: February 4, 2016
The monthly recovery indicators were uneven again. The NASDAQ fell almost -7% in the last month, and ISM non-manufacturing new orders and imports also declined. Full Analysis
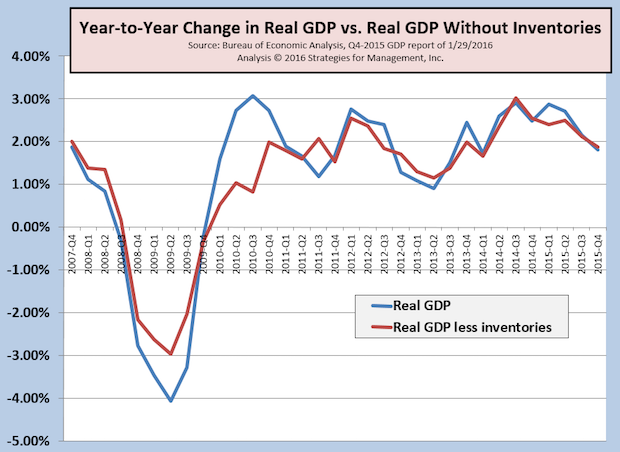
4Q-2015 GDP Disappoints at +0.7%; 2015 GDP +1.8%
Published: February 1, 2016
Real Gross Domestic Product (RGDP) for the US increased by an annual rate of +0.7% in the fourth quarter of 2015. On a year-to-year basis, RGDP was up +1.8%. Full Analysis
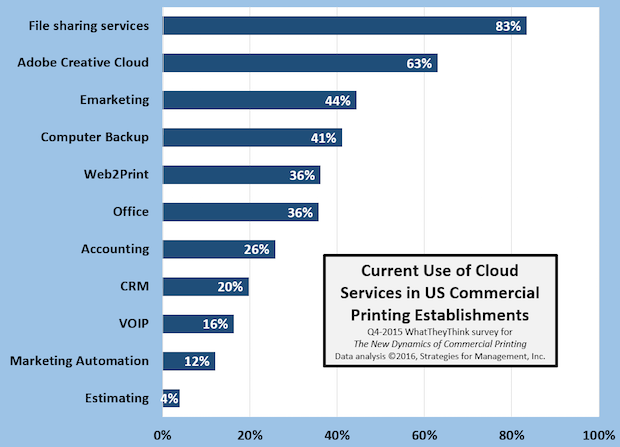
Cloud Product Usage in the Printing Industry
Published: January 28, 2016
The chart shows the percentage of US commercial printing establishments of all sizes and their responses to the question about the cloud-based services they use today. The question did not ask them their frequency or intensity of use, just whether or not they use it today. Some of the “non-users” may not even be aware that they are using cloud services, since some services run transparently in the background, such as backup services like Carbonite and others. Others may not be aware that they are using a VOIP phone system. Some cloud services such as Dropbox allow customers to brand their service so it looks like a company file sharing site. Generally, larger printers are using more cloud services than others, but the disparity is narrow. Full Analysis
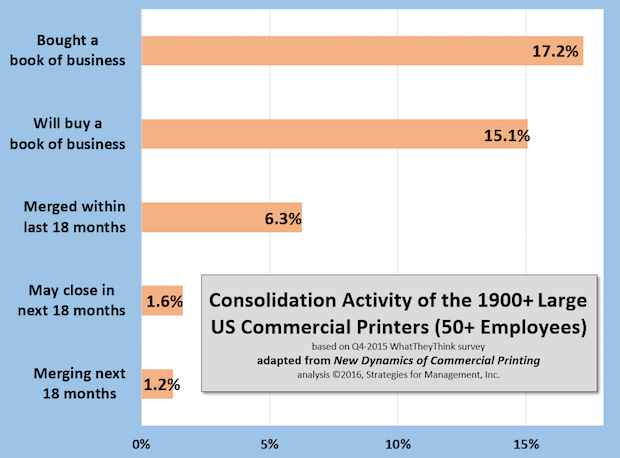
Consolidation is Somewhat Different Than Industry Common Wisdom
Published: January 21, 2016
Here are data from our survey at the end of 2015 where we asked respondents to identify the status of their companies in terms of consolidation. Generally, formal consolidations are executed by the largest print businesses, and small businesses close their respective shops and reopen a new business with new partners. Full Analysis
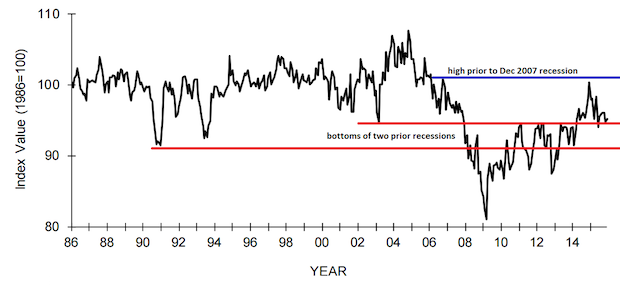
NFIB Small Business Index Still Shows Weak Small Business
Published: January 14, 2016
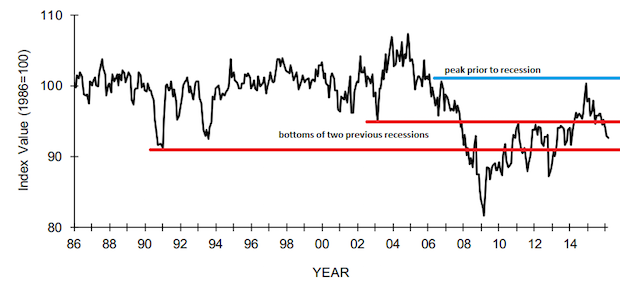
The latest survey of NFIB shows their index bouncing along the level of the early 2000s recession low, and down from the high prior to the December 2007 recession. Passing that level on the way up would have indicated a completed recovery of this sector but it just couldn't make it that far and break through. Using this indicator that means that small business did not emerge from the recession yet. Big business and the stock markets dominate the headlines, but small business remains the front line of the economy, and its difficulties are often hidden from view as being un-newsworthy. Its breakout above the bottom of the early 2000s recession took some time, and the recent trend in the chart looks like it's getting ready to fall below that again. It dipped below that level briefly a few months ago and climbed back out. Will it climb out again? It's worth watching. Full Analysis
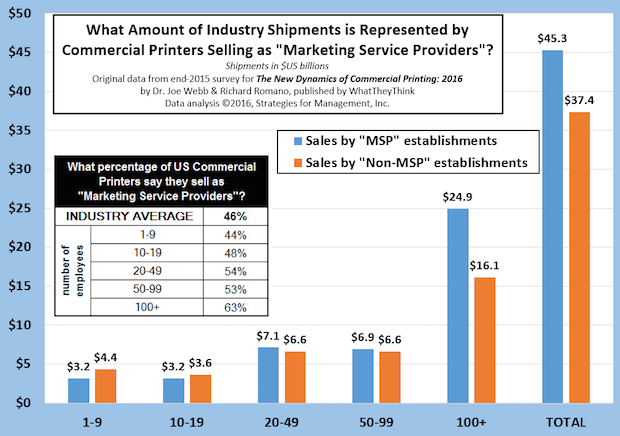
What Share of Shipments is Sold by “Marketing Service Providers”?
Published: January 7, 2016
For about a decade, many print businesses have marketed themselves as “marketing services providers” with varying degrees of success. Our recent survey showed less than half of print businesses market themselves in this or a similar manner. Full Analysis
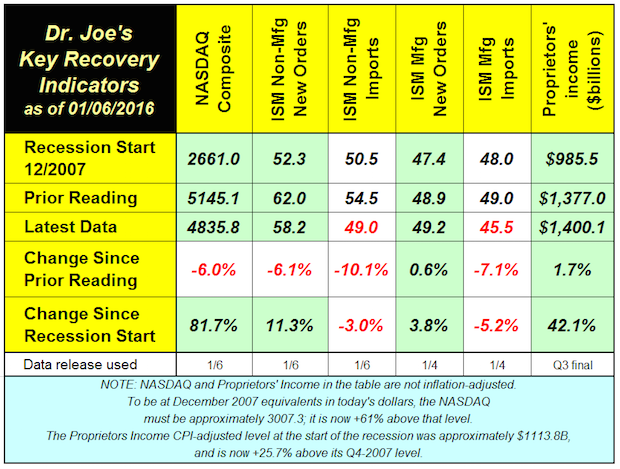
Recovery Indicators Look More Like Recession Indicators – Are They?
Published: January 6, 2016
Are the recovery indicators becoming recession indicators There's enough negative news of late to be wary about the state of the economy, and a lengthening list of geopolitical issues, for sure. Full Analysis
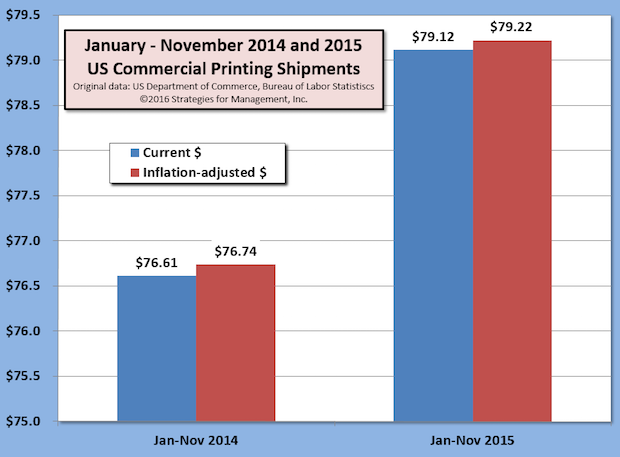
Eighteen Months of Industry Growth, Beating the Economy, Too
Published: January 6, 2016
US commercial printing industry shipments are up for 18 consecutive months in current dollars compared to the corresponding month of the prior year. Full Analysis
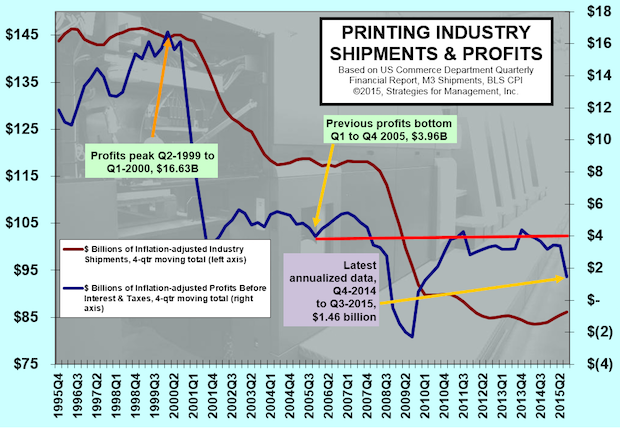
Printing Profits Dive as Large Printers Have Massive Writedowns
Published: December 22, 2015
The third quarter of 2015 marked a huge divergence in the performance of the industry, according to the Department of Commerce Quarterly Financial Report. Printers with more than $25 million in assets wrote down assets amounting to nearly -15% of revenues. This sent the quarterly moving total of inflation-adjusted profits before taxes to +$1.46 billion. Full Analysis
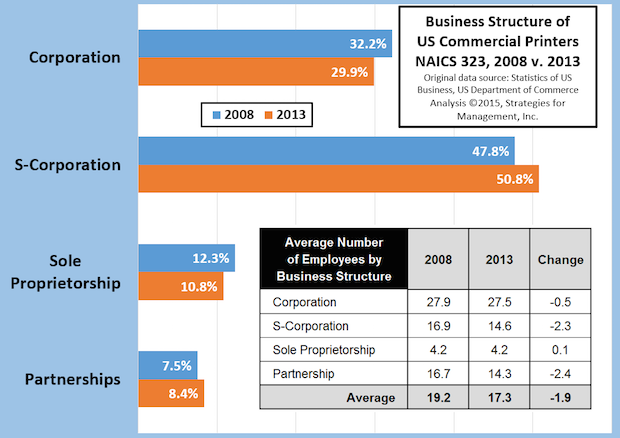
How the Business Structure of Commercial Printers Changed from 2008 to 2013
Published: December 17, 2015
The recession started just before 2008 was beginning and the latest data from the County Business Patterns report shows how the business formats of the industry changed by 2013. Full Analysis
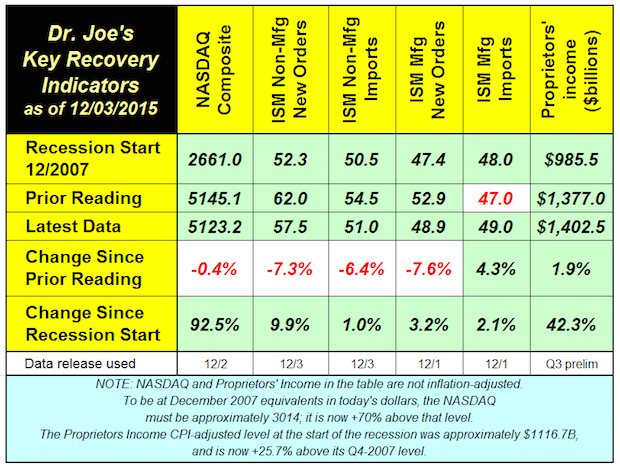
Recovery Indicators Cause Concern
Published: December 3, 2015
The recovery indicators turned in a mixed performance that warrants some caution, concern but not worry, yet. Some outside economic analysts starting to raise concerns about the economy in 2016. Citibank analysts peg the chances of recession in 2016 at 65%, the first such prognostication of a major investment firm that we have seen. Full Analysis
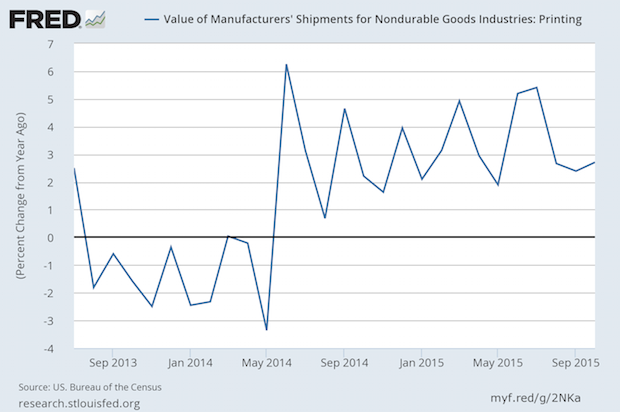
US Commercial Printing Shipments Have a Strong October, +$204 Million
Published: December 3, 2015
For 17 consecutive months the US commercial printing industry has scored increased shipments compared to the same month of the prior year. In current dollars, the Commerce Department reported that shipments were $7.729 billion. That meant that October 2016's shipments were +$204 million compared to 2015, a +2.7% performance. For the year through October, shipments are +3.3% on a current dollar basis. Full Analysis
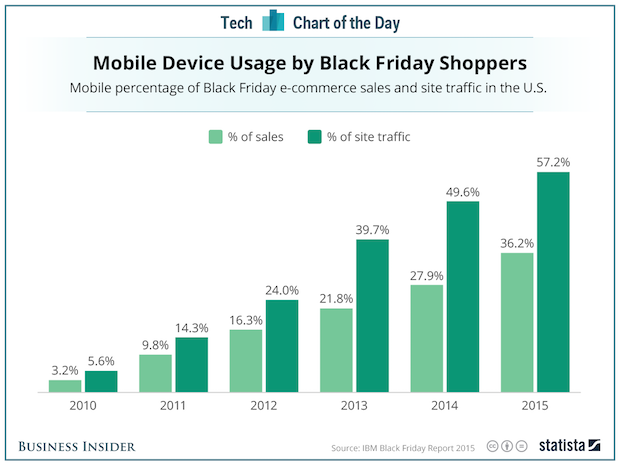
Mobile Plays Big Role in Black Friday
Published: December 3, 2015
The rise of mobile marketing has been long expected, and it looks like Black Friday 2015 is key milestone: mobile was more than half of web site traffic for e-commerce sites. Black Friday “brick-and-mortar” traffic was disappointing, but retailers were aggressively pushing sales online because it reduces the risks of riot-like runs for bargains as stores open. Target Stores had so much online traffic for CyberMonday its servers could not handle the volume. It wasn't the first time that Target misforecast demand for online sales. Some of Black Friday shopping may have been “window shopping” for mobile ordering. IBM, which still has a big business in systems for retailers issued a free download report about what was learned on Black Friday. In that report is the chart we highlight this week. If you sell to retailers or to businesses that sell to retailers, the report is worth reading. Full Analysis
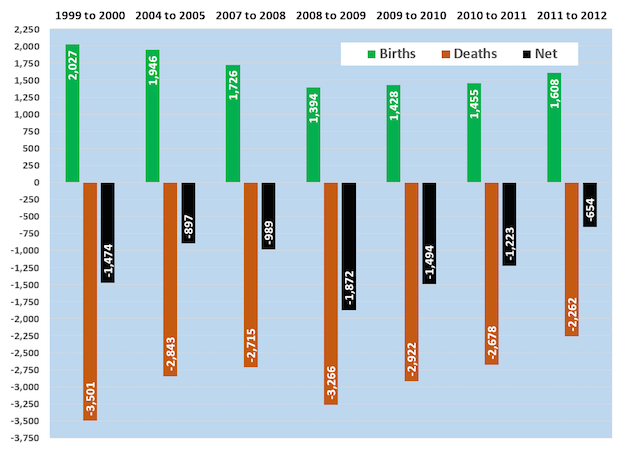
Printing's Birth-Death Data Show Improving Industry Health
Published: November 19, 2015
Even the usual industry dynamics are dynamic. The latest commercial printing industry birth-death data comparing 2012 to 2011 show a rising birth rate and a declining death rate. The +1608 births and -2262 deaths in 2012 were recent lows, as was the net change of only -654 establishments. Full Analysis
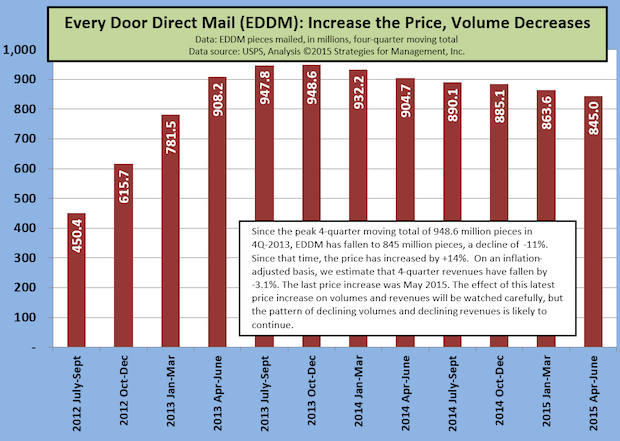
USPS EDDM Volume Decline Continues
Published: November 13, 2015
What could be an important product for local retailers to make their baby steps into direct mail, keeps declining as the USPS raises prices on the Every Door Direct Mail (EDDM) service. Full Analysis
Recovery Indicators Bounce Back
Published: November 9, 2015
The recovery indicators had a better month than last. Five of the six indicators increased and one fell below the level of the start of the recession. New orders for manufacturing and non-manufacturing were impressive in their increases, in stark contrast to government reports about September's durable goods and factory orders. Full Analysis
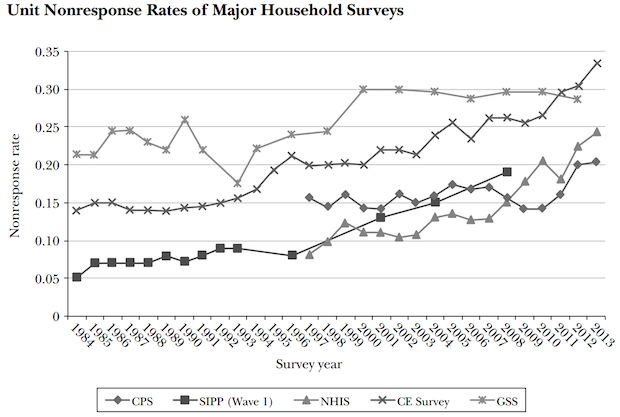
Can We Trust Government Data?
Published: November 5, 2015
A recent academic paper published in the Journal of Economic Perspectives (Volume 29, Number 4, Fall 2015), “Household Surveys in Crisis,” illustrates the problems of government surveys that are used to make multibillion dollar and multiyear decisions of government and business. Full Analysis
- Innovations in Inkjet for Textile Production – live webinar
- Buying Inkjet Part 1: Does This Printer Make Me Look Good?
- LabelExpo 2023: Launches and Trends – Part 2
- Driving profitability with cut-sheet inkjet
- Zero Trust Environments for Inkjet Printing
- Kevin Roman on the evolution of professional services needs
- LabelExpo 2023: Launches and Trends – Part 1
- Inkjet Gets into “Hard Core” Applications
© 2023 WhatTheyThink. All Rights Reserved.